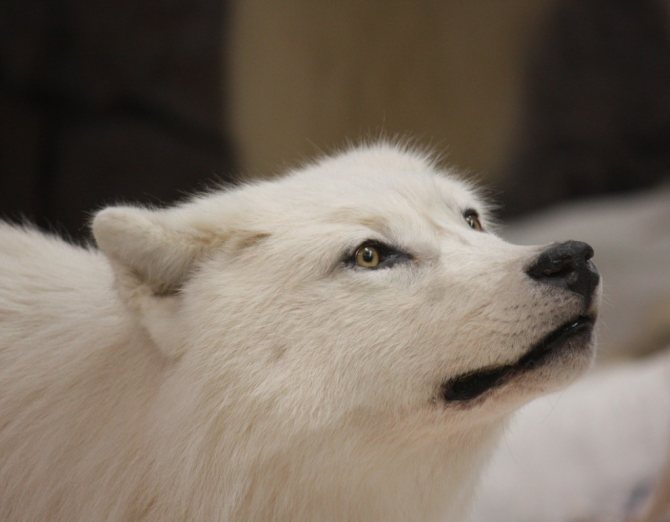
Appearance
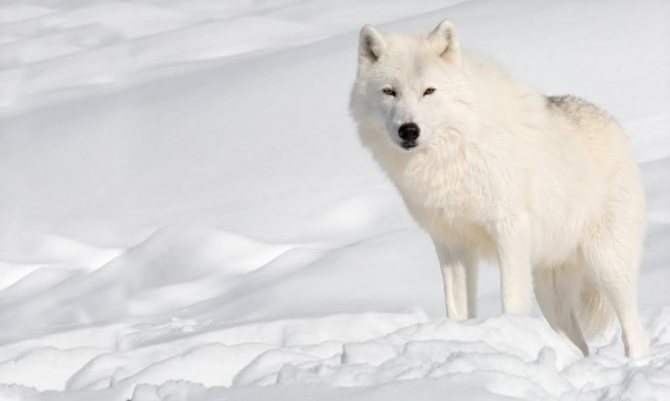
Polar wolves are quite dimensional mammals. Their body size reaches about 180 meters in length with a height of 100 centimeters. Body weight ranges from 85 to 92 kilograms. Sometimes polar wolves can be quite large, but the number of such representatives is quite small.
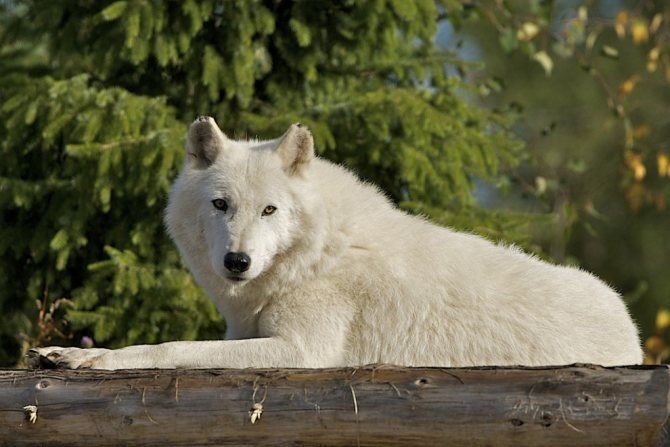
Sexual dimorphism is that females are 15 percent smaller than males. The distinctive fur of polar wolves is characterized by a strong dense and white coloration, which has a reddish hue. The limbs are muscular and long. The tail is short, covered with thick and lush fur.

Habitat conditions
The habitat of polar wolves is concentrated in the Arctic tundra, except for the ice spaces. These representatives can also be found in the dark polar areas. Animals have adapted to the harsh conditions of the Arctic, due to which they are able to withstand low temperatures for a long time, often starve and have no access to sunlight.
At this point, these predatory animals have inhabited the most barren areas of the earth. Temperatures have not risen above - 30 degrees Celsius since April, and the entire area is exposed to strong and gusty winds. Very few mammals sustain life in the Arctic.


Can the color change
Wolf's eyes are yellow in humans (photos taken at different times help you see changes in hue), as well as other shades may change with age in such cases:
- In children. Most newborn babies have a light green or blue-gray color. Closer to 6 months of age, the color of the eyes changes due to the accumulation of melanin - the iris becomes darker. By one year of age, the child's eyes take on the color that was determined genetically. But the final iris shade is formed closer to 5-10 years.
- At an older age. There is a process of depigmentation in the iris and the color of the eyes becomes duller, and sometimes may take on a lighter shade.
- In adulthood, under the influence of certain factors.
In the latter case, the change in eye color is influenced by:
- Physiological factors.
- External factors. These include the environment where the person is, weather conditions, changes in temperature, changes in light, color of clothing. The greatest ability to change the hue have lighter eyes.

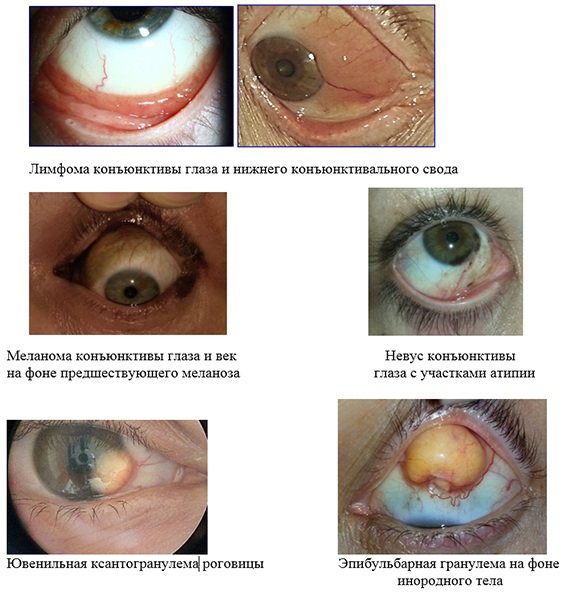
Physiological causes of eye color change are also divided into 2 groups, which are described in the table below:
| Natural factors | Pathological factors |
| Tears. Tears cause the iris of the eye to take on a more saturated hue. As a result of abundant moisture, the protein of the eye becomes lighter, tinting the color of the eyeball - the eyes take on a darker hue. | Lymphoma is a disease that affects the eye from the inside. The iris of the eye becomes dull, and visual acuity decreases. |
| Emotions. With strong emotions and other feelings, a person's pupil involuntarily dilates or contracts, resulting in a change in color of the eyes. Scientists believe that this is directly connected with the hormonal background. | Melanoma is a tumor that causes clouding of the cornea. As a result, the eyes may take on a dark brown hue. |
| Glaucomocytic crisis contributes to a dramatic darkening of the iris. A person has a fear of light, heaviness in the eyes, blurred vision, and multi-colored circles appear before the eyes. | |
| Fuchs syndrome. One eye is usually affected - it becomes darker than the healthy eye, the iris pattern is distorted, and the lens becomes cloudy. | |
| Horner syndrome is a pathology associated with damage to the nervous system. The disease is accompanied by a difference in eye color, drooping of the upper eyelid, and constriction of the pupil. |
It is not always the case that different eye colors in the same person may indicate a health problem. If heterochromia (different color of the iris of the right and left eye, or different shades of certain areas of one eye) is congenital, there is no reason for concern.
This phenomenon is very rare - different eye color have less than 1% of the population.


Yellow wolf eyes may become a consequence of heterochromia
Heterochromia is caused by such factors:
- Uneven distribution of pigment (melanin) in the shell.
- Lack or excess of melanin (one eye may have more or less of it compared to the other).
Complete heterochromia is more common (e.g., the right eye has a brown hue and the left eye has a blue hue). Less often, partial heterochromia may be observed, in which the iris of one eye has several different colors.
The latter variant is most often a consequence of hereditary diseases. To prevent the development of a number of eye diseases, it is still better to consult an ophthalmologist in case of heterochromia.
Nutrition
Because the Arctic consists almost entirely of open spaces, polar wolves can lurk to grab their prey unexpectedly. Their main food is musk oxen and reindeer. Less frequently, the wolves' diet includes small lemmings and polar hares. Hunting is done in packs. If a herd of musk oxen runs near the wolves, they give chase. During this time, the musk oxen manage to take up a circular defense. Then the animals have to wait, as they will not be able to break through the barrier of horns and hooves.
Polar wolves can arrange their runs around the herd, and as a result, the sheepdogs can change their position by breaking the circle. However, this tactic does not always work. If they manage to do so, however, the musk ox becomes quite easy prey. The wolves go in pursuit of a single prey and then grab it with a joint effort and roll it to the ground.


With the onset of winter, organized packs of polar wolves begin looking for places with a more favorable climate where they can find their prey. They migrate south following packs of reindeer. If a polar wolf has not had access to food for a long time, it eats about 10 kilograms of meat. Carcasses are dismembered with their powerful canines, and the meat is swallowed almost immediately.
Photos of wolves
About wolves.
"Ruthless and bloodthirsty predator" - such a description of the wolf can be found in almost any thematic publication, but few people realize that the "sanitary of the forest" is not just a killer, but a graceful, loyal to his pack animal, which can set an example to man as well.


Over several hundred years the number of wolves has fallen several times, because throughout time people have exterminated them for fun or to protect their livestock, not realizing that this predator is an indispensable link in the ecosystem and food chain.


Now many species of the canine family have been exterminated, and some are included in the Red Book. There are several breeds of wolves around the world, such as the common wolf, tundra wolf, red wolf, Tasmanian wolf, and others.
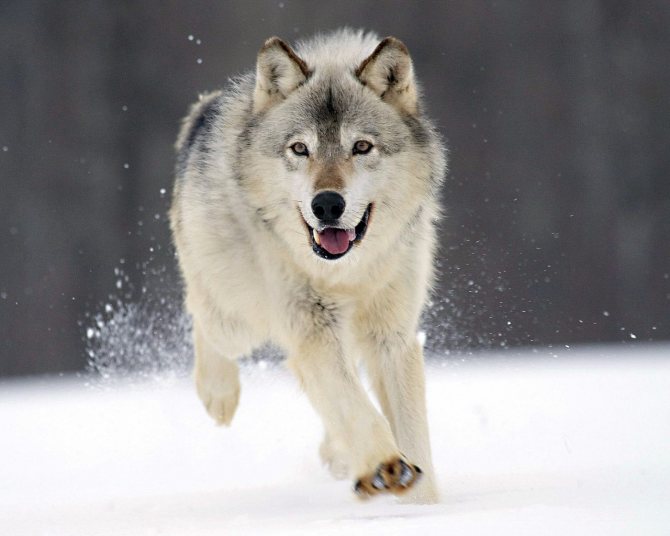


The body length of the wolf is about 150 cm, the height at the withers is 100 cm, and the average weight of the predator is 60 kg.
All 32 subspecies differ only in body size and coat color, but character and will are inherent in each of the representatives. "A wolf is much weaker than a lion or a tiger, but he, unlike them, does not perform in a circus." - Such a famous saying gives a full understanding of the essence of this proud animal.
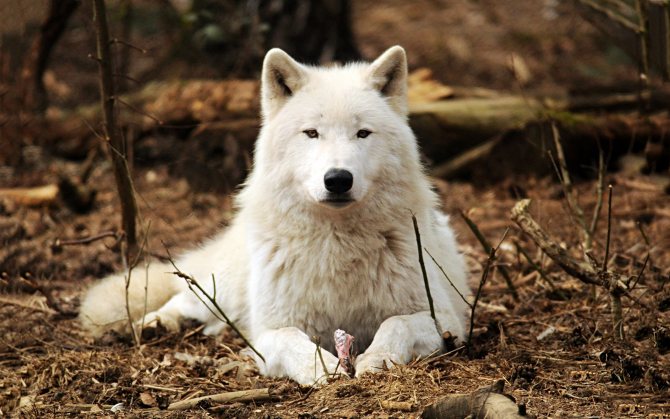


Depending on the habitat, the color of the animal's fur changes. If it is a desert, its hair has a red tint, if it is forest, then it is gray-brown, and if the snowy expanses, then it is white.
The wolf's hair consists of two layers. The first is the undercoat, which ensures the preservation of heat, and the second is the tough hair, which prevents moisture and dirt from penetrating the hide.


Newborn wolf cubs, regardless of species, always have a black color, which will turn into its own unique color over time. The eyes of the cubs are blue, but they will also change their color, turning golden-red or yellow. There have been cases when an adult wolf with blue eyes has been recorded, but this is extremely rare.
The wolf's adaptability to surviving in the forest or steppe is very high. Thick fur keeps the wolf from freezing, because the heat output is much higher than, say, even in the beaver.


Wolf feels great on a slippery surface due to the structure of the paw: the presence of bristly fur and blunt claws eliminates slipping, and wide blood vessels that run throughout the foot does not give it frozen.
A wolf's footprint can be unmistakably distinguished from that of any other animal thanks to the two middle toes, which visibly protrude.
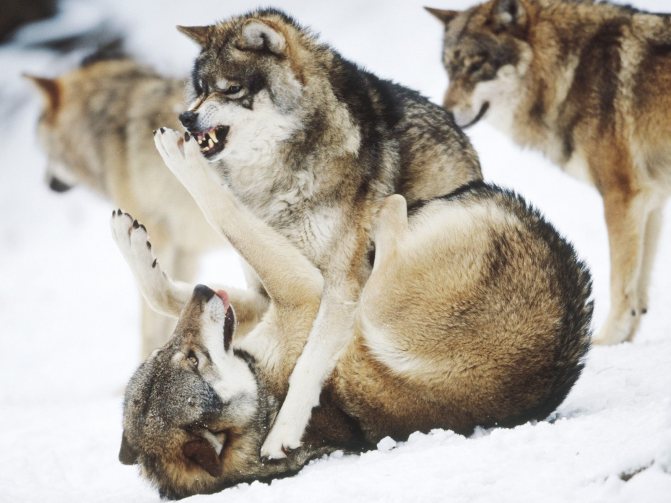


Each individual has special glands between the toes that secrete a certain enzyme with an odor. It helps to navigate their tracks better and also informs about the whereabouts of the leader or any other member of the pack.
Wolves are very hardy. Having strong paws, the animal can cover a distance of up to several tens of kilometers in a day, with a speed of about 10 km/h. In case of danger or in pursuit of prey, the wolf can develop a speed of up to 60 km / h.


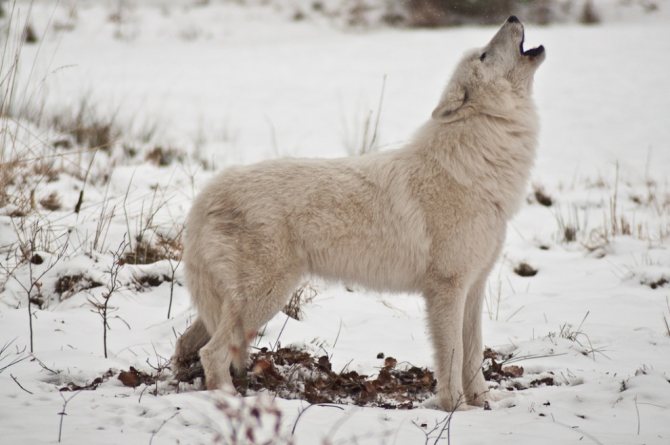
Information between members of the pack is conveyed by voice "messages", such as growling, long howls, growls, yapping and even "whimpering". Wolves also have excellent hearing, so the howls are heard by everyone within a radius of 8 to 10 kilometers.
Predators hunt mainly in packs. Most often wolves select weak or sick animals, but together they can attack a healthy 450-kilogram moose. The pack leader is the first to eat and needs about 6 kilograms of meat, while the rest of the pack waits for their turn. After a hearty meal, the pack lies down to rest, and some wolves begin to "sing" for a long time. Scientists have not yet been able to figure out what their song is about.
There are also pictures of black wolves.
There is also a unique mane wolf.
See gifs with wolves.
Gifs of angry wolves.
There are more pictures of a wolf and a she-wolf.
Breeding period.
The breeding period begins in March. Pregnancy lasts about 63 days. On average, 4 cubs are born. The offspring are borne only by the female leader, who is chosen among the other females of the flock. If another female gets pregnant, her litter is immediately destroyed. This is due to the lack of food in their territory, which prevents wolves from having many offspring.
After the mating season is over, the female separates from the pack and searches for a safe haven. Sometimes it establishes it on its own, but most often it inhabits rock crevices. The cubs emerge very weak, weighing no more than 410 grams at birth.
Young polar wolves spend their first time with the female. She feeds them with milk, and at one month of age, they begin to eat half-digested meat belched out by the male. While the female is busy caring for and keeping an eye on the cubs, the male goes in search of food. If the polar wolves are well fed, they quickly get on their feet. With the onset of summer, they join the pack of adult wolves. At 3 years of age, the animals become sexually mature.


Polar wolf with a pup
Does eye color affect their health
There are many studies around the world that aim to link eye color to a person's physical health.
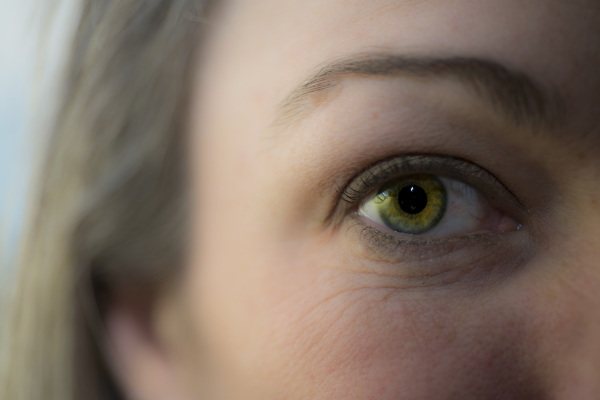


Some of them have proven that:
- The possessors of light eyes (blue eyes in particular) have a high pain threshold compared to dark-eyed people.
- Bright-eyed people have light-colored irises, which increases the risk of ultraviolet eye damage compared to dark-eyed people.
- Brown-eyed people have faster reactions, so they may be more successful than blond-eyed people in various sporting events.
- People with light eyes are more cold-blooded, so they often make deliberate and balanced decisions.
- Dark-eyed people compared to light-eyed people hop hop faster, but from the consequences of drinking and development of alcoholism suffered more all the same representatives of the light shade of eyes. This is due to the fact that the level of melanin in the eyes does not match the level of this substance in the brain, so to achieve intoxication light-eyed people need to drink more alcohol.
- Those with darker eye shade have a higher chance of getting cataracts at an older age.
- Bright-eyed people are able to recover more quickly from depression and other nervous system disorders compared to people with darker shades of eyes.
- Brown-eyed people, according to studies by psychologists, are more trustworthy than blue-eyed people.
Sometimes not only the pupil but also the eyeball may have an unusual color. For example, owners of dark brown eyes with a predominantly dark skin tone, the eyeball may be gray or yellow. The appearance of yellowing can indicate liver disease, particularly hepatitis. Most often, it can be a manifestation of hepatitis A directly.
As a result of the disease, there is an increased content of bilirubin in the body. During the breakdown of this substance, yellow spots appear on the eye whites (in normal health they have a white-milk color). The result is the release of a dangerous substance that has a negative effect on the activity of the nervous system.


In common parlance, hepatitis A is called jaundice.
Other causes of yellow coloring of the eyeballs may include:
- The defeat of liver cells by parasites;
- Development of malignant inflammatory processes of the eyes (e.g., conjunctivitis);
- cancer of the pancreas or gallbladder;
- development of anemia;
- Jaundice (most often in newborn children);
- hereditary liver disease (e.g., Gilbert's disease);
- thickening of the tissues of the eye (pinguecula);
- formation of growths in the eye (often found in the elderly).
- Taking certain medications;
- malaria;
- as a result of a transfusion of blood that is not suitable for the person;
- poisoning by poisons and other toxic substances.
Such changes can occur in people with any shade of eyes. Therefore, at the first sign of discoloration in the whites of the eyes, you should immediately consult a doctor.






















